Optimal LED Grow Light Distance: How Far Should It Be from Plants
Table of Contents
Introduction
Did you know? Improper placement of LED grow lights can slash plant growth efficiency by up to 50%! Whether you’re a beginner growing herbs at home or a seasoned professional managing a vertical farm, understanding the right distance between your LED grow lights and plants is crucial for success.
Why does it matter? Too close, and you risk leaf burn or heat stress; too far, and plants may suffer from weak, leggy growth. Striking the right balance ensures your plants get the optimal light intensity they need to thrive while maximizing energy efficiency and yields.
This guide will walk you through the key factors that affect grow light distance, including plant growth stages, light intensity, and practical tips to fine-tune your setup. Ready to unlock the full potential of your grow lights? Let’s dive in!
Why Grow Light Distance Matters
Maintaining the correct distance between LED grow lights and plants is essential for healthy growth, efficient energy use, and high yields. Here’s why:
1. Impact on Photosynthesis and Growth
- Plants rely on light to fuel photosynthesis, the process that converts light energy into food. The right light intensity directly influences photosynthetic efficiency and growth rates.
- 2024 Data Insight: Studies show that optimal LED placement can increase plant growth efficiency by up to 40%, significantly boosting yields.
2. Risks of Incorrect Placement
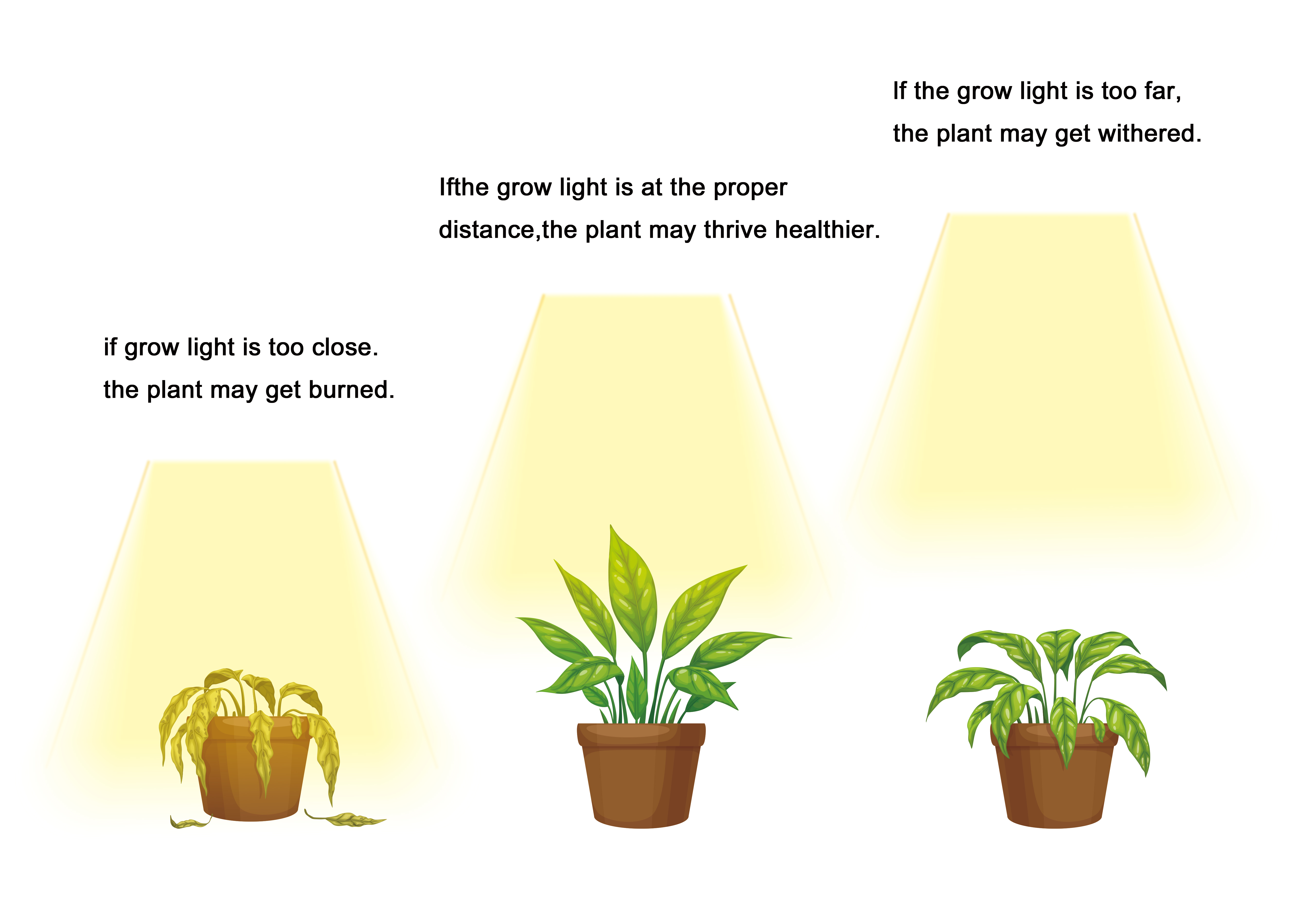
- Too Close: Excessive light intensity can cause leaf burn, heat stress, and stunted growth. For instance, young seedlings exposed to overly intense light often show curling leaves and discoloration.
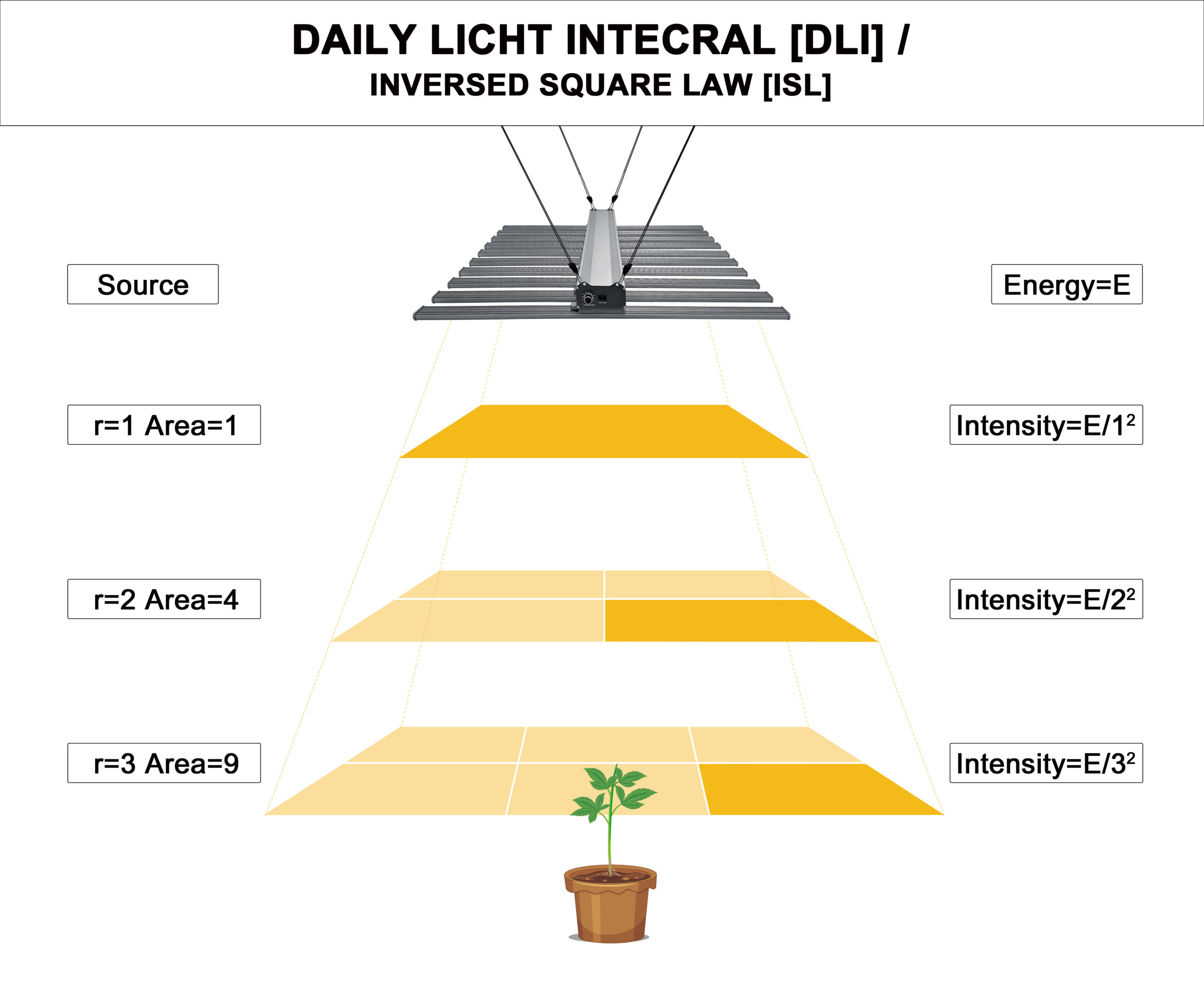
- Too Far: Light diminishes with distance (Inverse Square Law), leading to weak, leggy plants with low productivity. Poor light distribution can reduce yields by as much as 30%, particularly in dense canopies.
3. Energy Efficiency and Waste Reduction
- Correct light placement ensures plants receive the precise intensity needed, reducing wasted energy on non-productive areas.
- Case Study: A vertical farm using precise LED positioning cut energy costs by 25%while increasing crop yield by 20%, showcasing the dual benefits of proper distance management.
Below is a quick reference table summarizing risks and outcomes:
Understanding these effects will help you optimize your setup for better plant health and efficient resource use.
Factors Influencing Grow Light Distance
Proper LED grow light distance varies based on multiple factors, including plant growth stages, species, and light wattage. Understanding these variables ensures optimal light exposure for maximum plant health and productivity.
Plant Growth Stage
Each growth stage requires specific light intensity and distance to meet the plant’s changing needs:
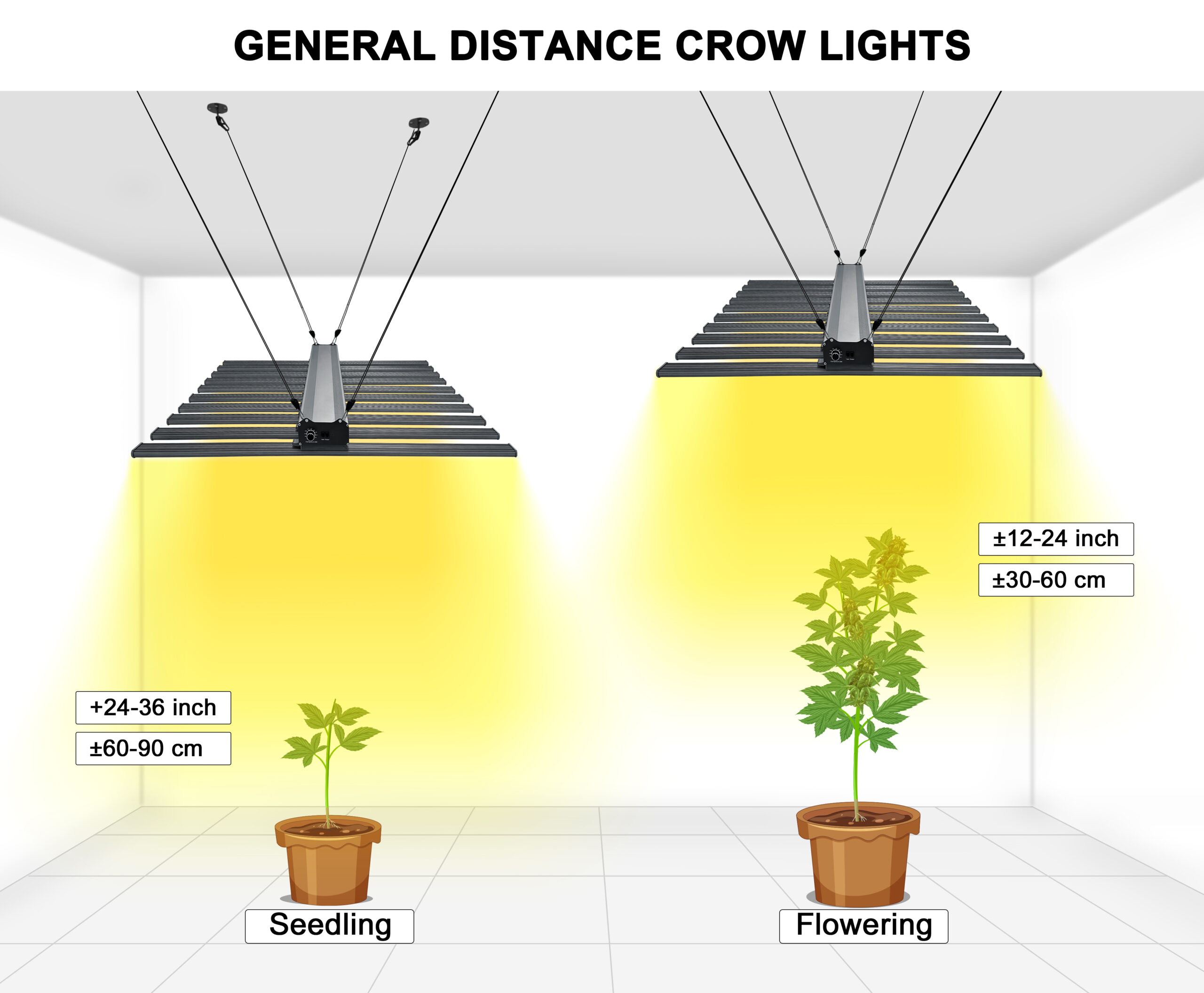
Seedling Stage
- Distance: 24–36 inches (60–90 cm).
- Reason: Protects delicate seedlings from excessive light while encouraging root development.
- Target PPFD: 100–300 μmol/m²/s.
- 2024 Insight: Research indicates keeping PPFD below 300 μmol/m²/s during this stage improves seedling survival by 25%.
Vegetative Stage
- Distance: 18–24 inches (45–60 cm).
- Reason: Provides increased intensity to promote vigorous leaf and stem growth.
- Target PPFD: 400–600 μmol/m²/s.
Flowering Stage
- Distance: 12–18 inches (30–45 cm).
- Reason: High-intensity light encourages flowering and fruit production.
- Target PPFD: 700–1000 μmol/m²/s.
- Fact: Studies reveal that flowering plants exposed to a PPFD of 800 μmol/m²/syield up to 15% more fruit compared to lower intensities.
Plant Species
Different plants have varying light requirements depending on their growth habits:
- Leafy Greens(e.g., lettuce, spinach):
- Tolerate closer distances due to lower light needs.
- Orchids and Herbs(e.g., basil, thyme):
- Require moderate intensity for steady growth.
- Flowering Plants(e.g., cannabis, tomatoes):
- Thrive with higher PPFD values to maximize yield.
- 2024 Update: Flowering plants show a 20% yield increaseunder targeted PPFD settings above 700 μmol/m²/s.
Grow Light Wattage
The power of your LED grow light also determines the appropriate distance:
Low Power (100–300W)
- Distance: 12–24 inches (30–60 cm).
- Example: Ideal for small herbs or microgreens.
Medium Power (400–600W)
- Distance: 18–30 inches (45–75 cm).
- Fact: Balancing heat and light distribution in this range prevents hotspots.
High Power (800W+)
- Distance: 24–36 inches (60–90 cm).
- Insight: Advanced cooling systems in modern 800W LEDs reduce heat, allowing closer placement without damage.
Correct distance management tailored to plant needs and wattage ensures healthy growth, minimizes energy waste, and maximizes yield potential.
How to Measure Light for Plant Growth
Accurate light measurement is essential for optimizing plant growth and ensuring proper LED placement. Here are the key metrics and tools to consider:
1. PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation)
- Definition: The range of light wavelengths (400–700 nm) that plants can use for photosynthesis.
- Importance: PAR ensures the light spectrum matches what plants need for energy production.
- Fact: In 2024, studies confirmed that light within this spectrum improves chlorophyll efficiency by 30%, compared to non-PAR wavelengths.
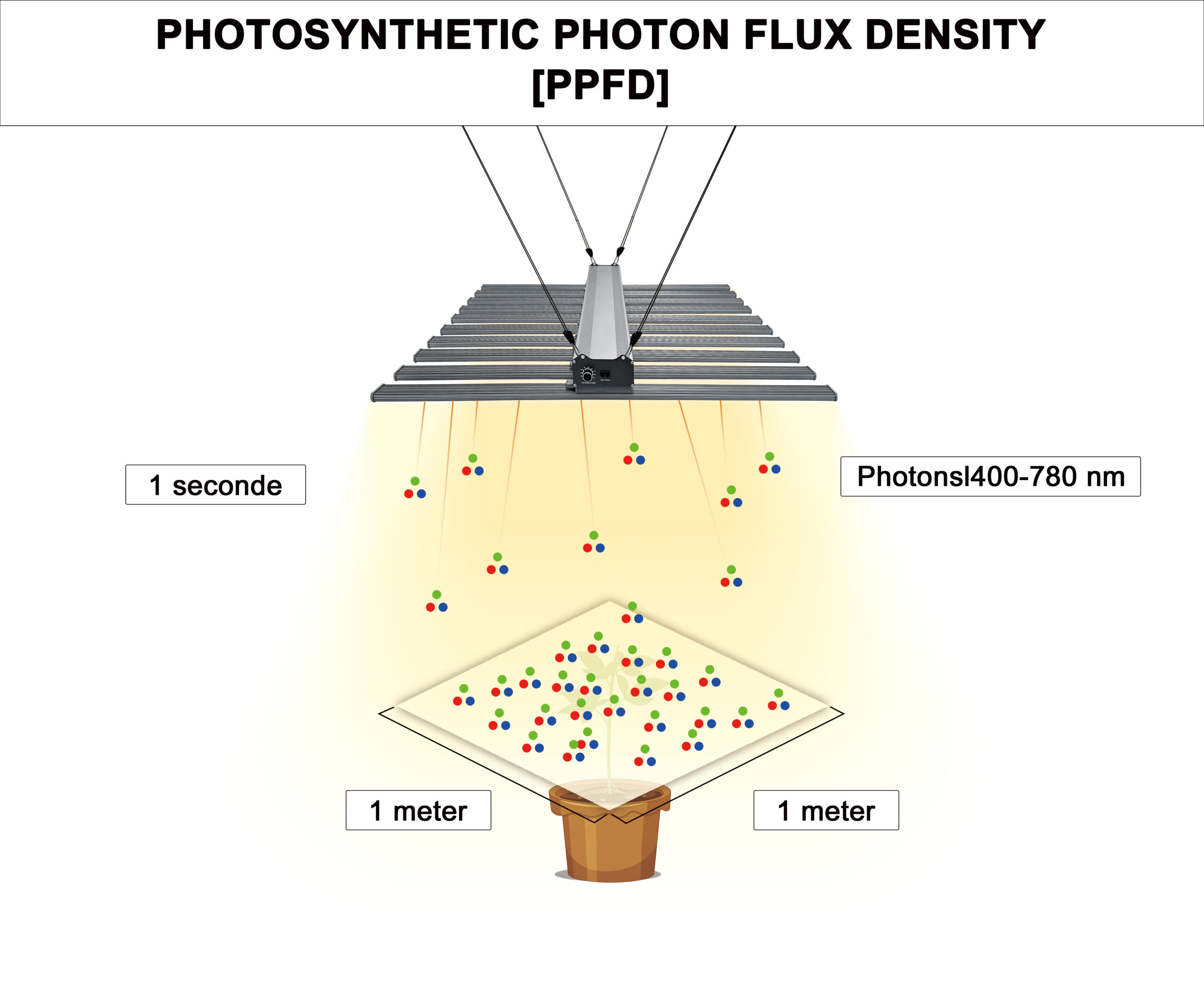
2. PPFD (Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density)
- Definition: Measures the intensity of PAR light reaching the plant’s surface (in μmol/m²/s).
- Why It Matters: Different growth stages require specific PPFD levels:
- Seedlings: 100–300 μmol/m²/s.
- Vegetative: 400–600 μmol/m²/s.
- Flowering: 700–1000 μmol/m²/s.
- Tip: Regularly monitor PPFD to avoid under- or over-lighting.
3. DLI (Daily Light Integral)
- Definition: Total amount of light received in a day, calculated as the sum of hourly PPFD over 24 hours.
- Significance: Ensures plants receive adequate light energy for photosynthesis over time.
- Example: Leafy greens thrive with a DLI of 12–17 mol/m²/day, while flowering plants may need up to 30 mol/m²/day.
- 2024 Insight: Advanced DLI monitoring systems are now integrated into high-end LED grow lights, enhancing real-time light adjustments.
Tools to Measure Light
Accurate light measurement requires specialized tools:
PAR Meters
- Measure PAR and PPFD values.
- Example: Apogee MQ-500, known for precise PAR readings, is popular in both commercial and home gardening setups.
DLI Meters
- Track cumulative light exposure over 24 hours.
- Fact: New sensors on the market now integrate Bluetooth connectivity for mobile data tracking.
Light Apps and Software
- Cost-effective for quick checks, though less accurate.
- Suitable for beginners or small-scale growers.
Investing in reliable tools ensures your plants receive the precise light conditions they need, maximizing growth and energy efficiency.
How to Determine the Optimal Grow Light Distance
Finding the perfect grow light distance involves a balance of guidelines, observation, and adjustments. Follow these steps to ensure optimal results:
Step 1: Follow Recommended Distance Guidelines
- Start with Manufacturer Specifications:
- LED grow lights come with recommended distances for various wattages and plant stages.
- Example: A 300W LED light typically requires a distance of 18–24 inches during the vegetative stage.
- Why It Matters: Manufacturer guidelines are based on tested light intensity and heat output.
Step 2: Experimentation and Observation
- Monitor Plant Health:
- Signs of stress include:
- Light Stress: Leaf curling, discoloration, or burn marks.
- Insufficient Light: Stretchy, leggy growth with pale leaves.
- Adjust Accordingly:
- Raise the light if plants show signs of heat stress or bleaching.
- Lower the light to encourage compact, robust growth if plants appear weak.
- 2024 Tip: Modern LED systems with dimmable features allow fine-tuning light intensity without moving the fixture.
- Signs of stress include:
Step 3: Adjust Distance During Growth
- Adapt to Growth Stages:
- Plants require different light intensities at each stage.
- Adjust distances to maintain target PPFD levels.
- Example: During flowering, lowering the light from 18 to 12 inches can boost flower density by 15%.
- Consider Environmental Factors:
- Ensure good ventilation to prevent heat buildup.
- Reflective walls can enhance light distribution, reducing the need for closer placement.
Experimentation combined with consistent observation ensures your grow lights are always at the ideal distance, tailored to both plant needs and environmental conditions.
FAQs About Grow Light Distances
1. What Tools Can I Use to Measure Light Intensity?
- PAR Meters: Measure Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) to ensure light wavelengths align with plant needs.
- Example: The Apogee MQ-610 provides precise PPFD readings suitable for all growth stages.
- DLI Meters: Track Daily Light Integral (DLI) to monitor cumulative light exposure over 24 hours.
- 2024 Insight: New Bluetooth-enabled DLI meters simplify real-time tracking and data logging.
- Light Measurement Apps: Offer a quick, budget-friendly way to estimate intensity, though less accurate than dedicated tools.
2. What Signs Indicate My Grow Light Is Too Close or Too Far?
- Too Close:
- Leaf burn or discoloration (yellowing, browning).
- Curling leaves or crispy edges.
- Plants appear stunted or stop growing.
- Too Far:
- Stretchy, leggy growth as plants reach for the light.
- Pale or yellow leaves due to insufficient light intensity.
- Poor flowering or fruiting, especially in high-yield crops.
- 2024 Data: Studies reveal that maintaining PPFD within recommended ranges reduces leaf stress incidents by 30%.
3. Practical Troubleshooting for Light-Related Issues
Step 1: Check Light Distance
- Use the recommended guidelines as a starting point (e.g., 12–18 inches for flowering). Adjust as needed based on plant feedback.
Step 2: Monitor Environmental Conditions
- Ensure proper airflow to reduce heat stress. Use fans or adjust ventilation for optimal cooling.
Step 3: Adjust Light Intensity
- Dim the lights if signs of stress persist, or increase intensity for leggy growth. Many 2024 LED models feature adjustable wattage for precise control.
By using these tools and techniques, you can proactively address light-related challenges, ensuring your plants receive the optimal conditions to thrive.
Final Thoughts
Setting the right LED grow light distance is crucial for healthy plants, high yields, and efficient energy use. By understanding factors such as growth stages, plant species, and light wattage, you can optimize your grow light setup and avoid common pitfalls like leaf burn or insufficient light. With proper light placement, you’ll ensure your plants thrive at every stage of their development.
Ready to take the next step?
- Download our free Grow Light Distance Chartfor quick reference and practical guidelines tailored to your setup.
- Subscribe to our newsletterfor expert tips, the latest industry updates, and actionable advice on indoor gardening success.
Start optimizing your grow light distance today and watch your plants flourish!
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
CATEGORIES
Recommended Post

Where It’s Legal to Grow Cannabis: Ultimate Tips & Cultivation Laws
About Author—Jose Li
Jose, a senior content creator at BATA LED, brings over 5 years of expertise in LED grow light. He delivers valuable insights to help growers and farmers better understand LED grow light technology, empowering them to boost crop yields and quality with advanced lighting solutions.