Unlocking the Visible Light Spectrum: How to Maximize Plant Growth and Photosynthesis Efficiency
Introduction
Plant growth requires light, and knowing how to optimize the visible light spectrum can increase photosynthesis efficiency by a large order of magnitude. Thankfully, with advancements in LED grow lights, growers are given the opportunity to manipulate specific wavelengths to their advantage. However, what do different wavelengths do to plants, and what spectrum can I maximize for various growth stages? In this article, I deepen my knowledge into the visible light spectrum and its role in photosynthesis, and offer practical solutions for growers to employ the power of this light. This guide will equip you whether you’re a home grower or a commercial farmer with the knowledge to maximize yields.
Understanding the Visible Light Spectrum and Its Role in Plant Growth
What is the Visible Light Spectrum?
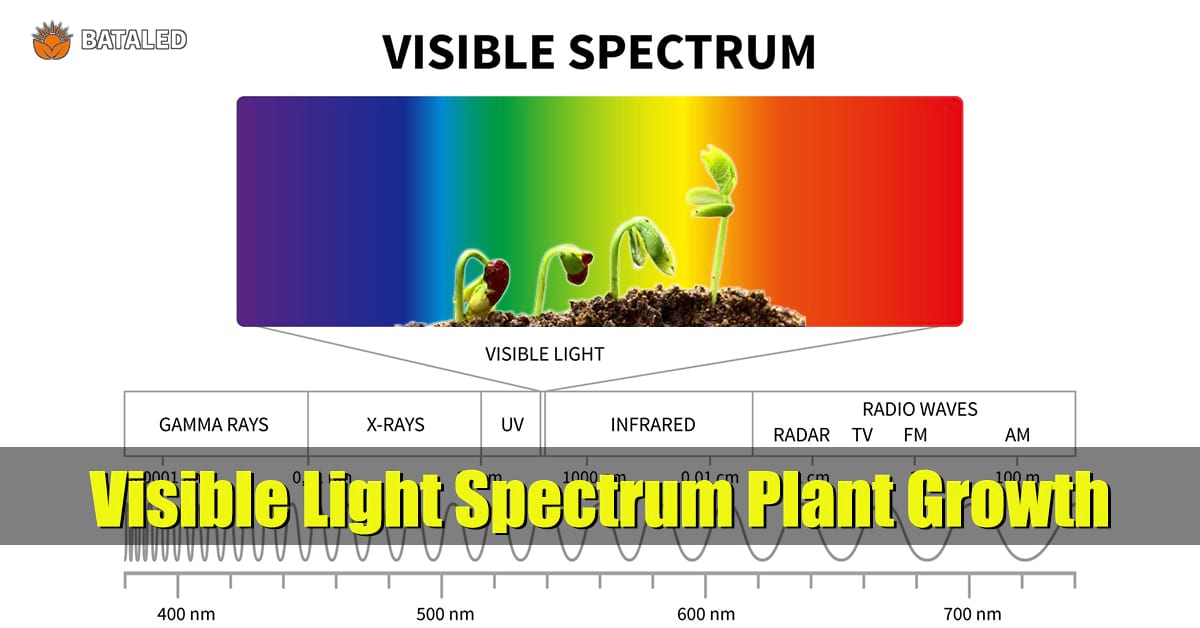
A visible light spectrum is composed of different wavelengths of light from 400 to 700 nm. There is a unique role of each color of light in this range in the plant growth. In that same section, we will explain what the visible spectrum is, and how plants react to different wavelengths.
Why is the Visible Light Spectrum Critical for Photosynthesis?
Plants absorb the different wavelengths within the visible light spectrum, and use it to fuel photosynthesis. This section will explain the science of how chlorophyll absorbs that it can turn the light waves into energy used by plants.
Different Light Wavelengths and Their Impact on Photosynthesis
Blue Light (450-490 nm): Best for Vegetative Growth
Vegetative growth, and especially leaf development, requires blue light. In this section we will explain how blue light helps enhance photosynthesis by stimulating chlorophyll production and thus an increase in robust leaf growth. Research shows that blue light exposure helps increase the plants photosynthetic rates and general vigor overall, making it important for juvenile plants in the vegetative state.
Red Light (620-750 nm): Essential for Flowering and Fruiting
Plant development requires red light for flowering and fruiting. In this section, the effects of red light on plant reproductive growth (stimulating flower formation and fruit set) is explored. These results provide proof that red wavelengths trigger phytochrome responses, required for signaling of the transition from vegetative to reproductive phases, and support higher yields.
Green Light (495-570 nm): Supporting Photosynthesis
Although green light is not absorbed as heavily by plants, it has a supportive role is photosynthesis. Next up, we will explain how green light allows for plant health and thus overall plant growth by adding more layers of depth to plant leaf layers for greater light utilization efficiency. Green light also turns out to stimulate photosynthetic activity under some circumstances, and to maintain this balance in plant growth.
UV Light (10-400 nm) and Its Role in Plant Health
UV light can make plants healthier, strengthened against disease and induce defense mechanisms. In this section we will consider how by putting plants under UV light we are stimulating production of secondary metabolites which can help protect against pathogens at a biochemical level. The benefit of UV exposure can be understood to help the growers to use it strategically to make plants more resilient.
Infrared Light (700 nm – 1000 nm): Stimulating Growth and Flowering
In fact, infrared light increases metabolism and promotes flowering in plants. In this part, we’ll talk about how infrared wavelengths keep plants growing faster by increasing respiration rates and energy available for flowering. In other research it has been found that using infrared light can add to improved flowering success and overall plant production making it an important part of a successful lighting strategy.
Optimizing Light Spectrum for Different Growth Stages
Best Light Spectrum for Seedling Stage
The blue dominant light spectrums encourage strong leaf development and later healthy growth of seedlings. When using LED fixtures, grow lights for your seedling development use those that emphasize wavelengths of 450-490 nm. Don’t allow the light intensity to be too high as this stresses the plants, or too close — you’ll burn tender seedlings. Watch for growth and adjust the amount of light exposure to give the best vigorous, robust plants from the get go.
Maximizing Photosynthesis Efficiency in the Vegetative Stage
During vegetative stage plants need to have a ratio between blue and red light for optimum photosynthesis. Next, we discuss how light spectrums can be fine tuned by addition of blue (450–490 nm) or red (620–750 nm) wavelength to increase growth rates. But a balanced light ratio of about 70 per cent blue to 30 per cent red can set up a good balance between strong stem and leaf growth. Furthermore, make sure your growing temps are optimal (for growing indoor, 18-22C [65-72F is good]); and light duration is sufficient, around 16-18 hours daily for optimum photosynthetic activity.
Achieving Maximum Yields in the Flowering Stage
Higher ratio of red and infrared light increases the flowering plants and helps them to maximize their yields. During flowering stage, this section will explain how to adjust light setting by raising the spectrum to around 60% red and about 40% of infrared. Wavelengths emitted by these lights, between 620 nm and 750 nm (blue to red), and the inclusion of infrared (700 nm to 1000 nm) can promote flower formation and fruit set. Keeping the light cycle in about 12 hours light and 12 hours dark is also necessary to trigger proper flowering process.
Practical Applications of the Light Spectrum in Indoor Growing
Full Spectrum vs. Targeted Spectrum: Which is Better?
Whether grow lights are best full spectrum or targeted spectrum is often a question growers ask. Varieties of full spectrum lights feature complete range of wavelengths that closely match natural sunlight, meaning they can be used for virtually all plant stages. Targeted spectrum lights focus on specific wavelengths, and feed more into specific growth phases. This section will explore the benefits of full spectrum versus targeted lights for crops, comparing the advantages of full spectrum for overall health against the efficiency of targeted lights for specific crops, and help you decide which approach to your growing environment is best.
Using Full Spectrum LED Grow Lights for Advanced Crop Yield
Full spectrum grow lights are full spectrum (meaning they mimic natural sunlight) so that plants have the full spectrum of wavelengths that are important for all growth stages. This section will explain how the better crop yields gained from using full spectrum LEDs promote healthy growth, greater photosynthesis and better overall plant vitality. We will break down benefits such as increased chlorophyll production, earlier flowering time and higher nutrient carrier in the final produce. full spectrum LEDs offer exactly these advantages making it an ideal lighting system, especially for novice and experienced growers, who are seeking high crop yields from the plants they’re growing.
Custom Light Spectrum for Leafy Greens, Tomatoes, and High-value Crops
The light spectrum needs of different crops can be very different, and will have a great impact on growth and production. In this part, we are going to elaborate on how to change your grow light settings for certain types of crop, like leafy greens, which need blue dominant spectra, or tomatoes, which need more red light at flowering. Changing the spectrum can optimize the nutrient content and quality of yield for high value crops. Tailoring your light settings to the particular demands of each crop means you’ll secure best possible growth and optimal harvests, usually with big returns on your investment.
Energy-efficient Techniques for Using LED Grow Lights
Dynamic Spectrum Control for Efficient Greenhouse Growing
Growers can choose how much of the light output to utilize, and thereby use more or less energy depending on the particular growth stages of their plants, thanks to dynamic spectrum control. This section will present how this technology may be used to deliver light in greenhouse environments. Growth rates for plants, as well as energy costs, can be drastically reduced by tailoring the spectrum to meet the changing needs of plant growth. Dynamic controls will be shown within real world examples which reduce lighting schedules for improved growing efficiency and wastage.
How to Maximize Yield with Minimal Energy Consumption
For many growers, yield is maximized with minimum use of energy. We will see some practical strategies for achieving this balance, optimized light duration, utilization of energy efficient bulbs, and the use of reflective material distribution of light. We will also discuss how we can monitor plant response to light, and if necessary, adjust such that robust growth occurs without excess energy expense. The adoption of these techniques can have a tremendous impact on savings and also sustainability in your growing methodology.
Eco-friendly Light Spectrum Choices for Sustainable Farming
With increasingly sustainable farming practices regaining importance, the selection of ecological and energy saving light spectrums becomes especially important. While this part will discuss how to use various eco friendly lighting (e.g. LEDs that minimize energy consumption). Next up we will discuss advantages of utilizing light spectrums which support plant health and reduce the carbon footprint. Now, growers can positively align agricultural practices with ecological responsibility by integrating sustainable lighting solutions which can assure not only high yields but also a contribution to a more environmental friendly environment.
Practical Tips for Home Growers
Best LED Light Spectrum for Indoor Vegetative and Flowering Stages
For instance home growers can achieve top leads by carefully tuning their LED light settings for different stages of growth. For vegetative, a blue dominant spectrum is needed for healthy leaf development, and a red and infrared spectrum is the key for flowering. In this section, we will discuss how to plant marijuana with practical tips like the optimal distance of lights to plants, most preferred light intensity levels and timing for light cycles to maximize plant health and mountainous yields in home environments.
User-friendly Guide to Maximizing Light Spectrum Efficiency in Home Grows
Setting up LED grow lights can be overwhelming for those that are new to indoor gardening. In this section, you will find a simple Checklist explaining in easy to read steps how to optimize your light spectrum efficiency. There will be discussion on selecting which type of LED lights to use, and where to place them as well as adjusting the settings to suit plant needs. In addition, suggestions on how you can keep track of your plants’ health and make the appropriate adjustments will aid in the thriving of an indoor garden as well as the plant health and yields.
Conclusion
The unlock to the full development and performance of plant development as well also the efficiency of photosynthesis lies within optimizing of the visible light spectrum. Knowing which wavelengths play what role and how you can use this knowledge to apply practical techniques can result in big improvements in plant yields, regardless if you are growing plants in a home garden or on a commercial basis. Want to fortify your farm already? But today start adjusting your light spectrum to see the difference. If you want more tips and more advanced growing techniques on our work-subscribe to our blog or leave a comment below.